Currently, there is no specific cure for Japanese encephalitis. However, symptomatic treatment, including medications, fluid, and oxygen, can help the individual fight off the infection.

You are now leaving GSK’s website and are going to a website that is not operated/controlled by GSK. Though we feel it could be useful to you,we are not responsible for the content/service or availability of linked sites. You are therefore mindful of these risks and have decided to go ahead.
Agree Agree Agree Stay
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection spread through infected mosquito bites. It is preventable through vaccination.
The vaccination against JE is not recommended for routine use, but only for individuals living in endemic areas.
JE vaccine is also recommended for travelers to JE endemic areas provided they are expected to stay for a minimum of 4 weeks in rural areas in the JE season
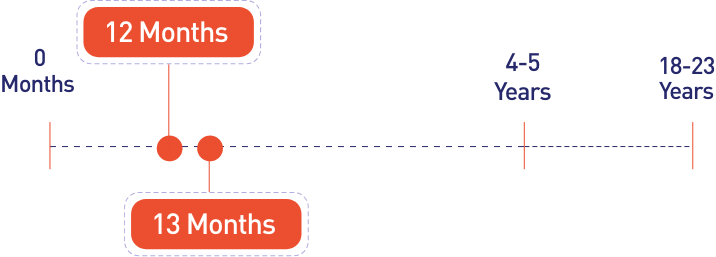
If you miss out the dose of these vaccinations during the stipulated time, you can consult with your doctor for a Catch-up Vaccination.
Consult your paediatrician for more information on Japanese encephalitis vaccination.
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection caused by a flavivirus. It spreads through the bite of mosquitos infected with this virus. The primary source of infection is found in pigs and birds that carry flavivirus, which then transfers to mosquitos when they bite on infected animals. The disease can cause brain swelling or damage in severe cases, leading to permanent brain damage. The mosquitos that carry the virus breed mostly in tropical areas, both rural and urban, including marshlands, pig farms, and paddy fields.
About one in four cases who develop severe complications die because of the infection.
This viral disease is transmitted from animals to humans by mosquitos. Pigs and birds are the primary carriers of this virus. When a mosquito bites any infected animals or birds, it gets infected with the virus. Now, if that infected mosquito bites humans, it passes on the virus, further causing the infection.
The virus does not spread through human contact or sharing of drinks or food.
Most people infected with the illness show no or mild symptoms, such as headache or nausea. The symptoms are usually mistaken for flu.
However, a tiny percentage of people infected with Japanese encephalitis develop complications as the infection spreads to the brain. Rarely a person with a severe condition may experience:
If the person with severe complications manages to survive, he may experience permanent brain damage, paralysis in one or two limbs, weak muscles, twitches, etc.
The Japanese encephalitis vaccine is usually recommended for children aged two months and above.
However, consult your doctor for more information.
The vaccinated person may experience mild and short-lived side effects, such as:
If the side effects persist, please consult your doctor.

Currently, there is no specific cure for Japanese encephalitis. However, symptomatic treatment, including medications, fluid, and oxygen, can help the individual fight off the infection.
A public awareness initiative by GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Limited. Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli, Mumbai 400 030, India.
Information appearing in this material is for general awareness only. Nothing contained in this material constitutes medical advice. Please consult your doctor for any medical queries, any question or concern you may have regarding your condition. The disease list indicated for vaccination is not complete, please consult your child’s Paediatrician for the complete vaccination schedule. The doctor shown in this material is being used for illustrative purpose only and is a professional model. The disease representation icons/images and animation are for illustrative purpose only.