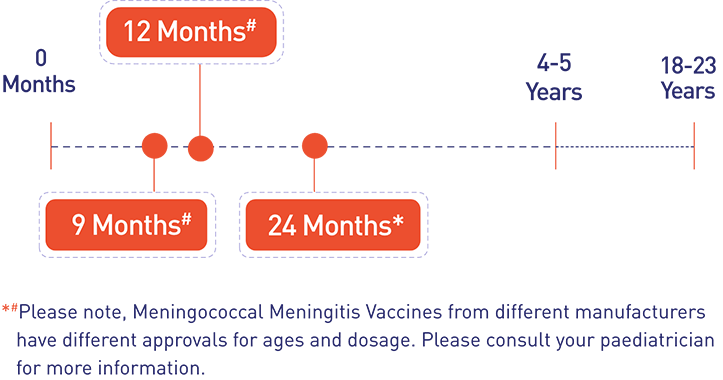
Meningococcal meningitis primarily affects the lining of the brain and the spinal cord and causes swelling. However, the symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the infection. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Stiff neck
- Confused mental state
- Photophobia (visual sensitivity to light)
One of the more severe forms of infection is meningococcal septicemia. This can show up as a dark purple rash and a rapid circulatory collapse, often proving fatal.
Complications:
Even with early diagnosis, about 8% to 15% of the patients may not survive the first 24 to 48 hours of the infection.
1 in 5 survivors can develop complications such as deafness, problems with the nervous system, brain damage.